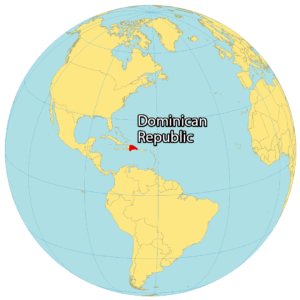
Where is the Dominican Republic located?
Millions of tourists visit the Dominican Republic each year to enjoy their beautiful beaches, outstanding cuisine, and check one of the most impressive landscapes the world can offer.
Most of you are first timers and got the word about the country by a friend, family member, or a coworker.
But first, you need to know where you are flying before making any plans.
Where is the Dominican Republic located?
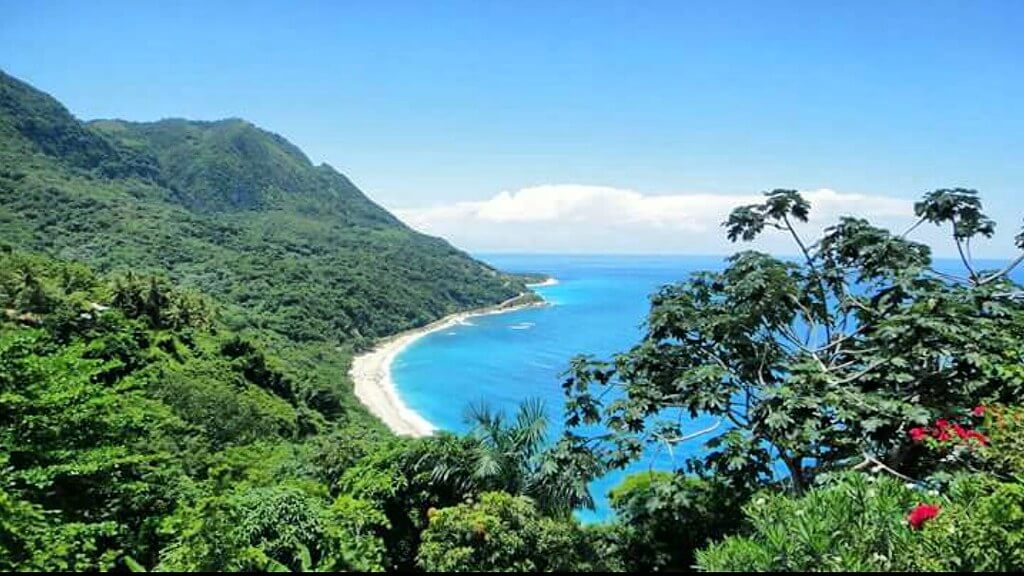
The Dominican Republic is located in the Caribbean, specifically on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago, and occupies the eastern two thirds of the territory that shares with Haiti, on the western third.
To give you an idea, it is about two times the size of Rhode Island or half the size of Sicily.
The island of Hispaniola is located in the middle of the Caribbean Sea, north of Venezuela and Puerto Rico and south of Cuba.
It is the second largest nation in the Caribbean with a surface area of 48,442 square kilometers (18,704 square miles).
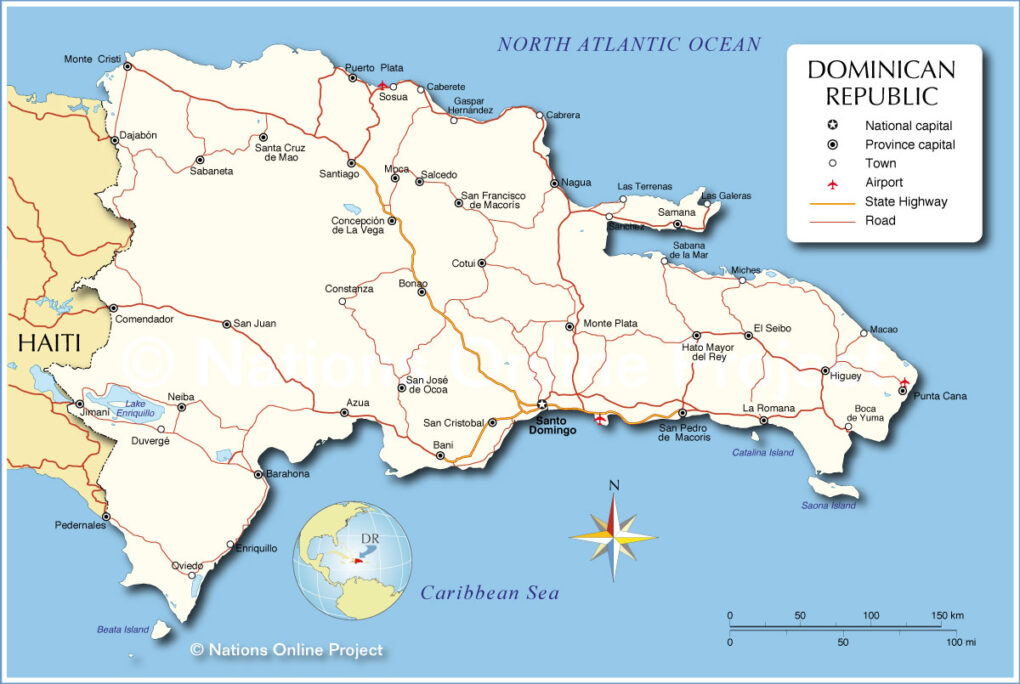
Dominican Republic Bordering Countries
The Dominican Republic bordering countries are:
- Haiti (west)
The Dominican Republic shares maritime borders with :
- The Bahamas (north)
- Turks and Caicos Islands (northeast)
- Puerto Rico (east)
- Venezuela (southwest)
Origin of the name “Dominican Republic”
The word “Dominican” comes from the Latin Dominicus, meaning “belonging to God”. “Republic” comes from the Latin res publica and means “public thing”. Therefore, the full name of the country means “God’s public thing”.
The Dominican territory was discovered by Christopher Columbus on his first voyage to America in 1492, who claimed it immediately for the Spanish Crown. He arrived at the island on December 5, 1492 and named it “La Española” in times of Spanish conquest, which means “The Spanish Woman” in English.
The Dominican Republic has a long and rich history. In pre Columbian times, the first inhabitants of the island were the Taino people, who arrived from South America around the 7th century AD. The Taino were a peaceful people who lived off agriculture from its fertile valleys and fishing.
The estimates of Hispaniola’s population in 1492 vary widely, including tens of thousands, one hundred thousand, three hundred thousand, and four hundred thousand. Determining precisely how many people lived on the island in pre-Columbian times is next to impossible, as no accurate records exist. [48] By 1492, the island was divided into five Taíno chiefdoms.
Spanish History
The Dominican Republic was the first country in America to be colonized by the Spanish, who built the colonial zone, or ciudad colonial, and within the majority of the first buildings in America, which include:
- The first cathedral – Catedral Primada de América
- University – Universidad de Santo Tomás de Aquino, the now Universidad Autónoma de Santo Domingo.
- Hospital – Hospital San Nicolás de Bari
Today, the Colonial Zone is filled with other treasures to explore, including the Ruinas de San Francisco, where live bands play salsa, merengue and bachata music on the weekends, the Puerta de la Independencia, the National Pantheon, and the Calle Las Damas, the oldest street in the New World.
The Spanish also introduced the use of tobacco and cattle to the island. For the next centuries following their first arrival, the colony was ruled by Spain.
French Colony
In the late 1600s, France conquered part of the island, which became known as Haiti, inhabited mostly by African slaves.
Spain recognized the French dominion and ceded the western part of the island to France in the Treaty of Ryswick in 1697.
The French colony, then called Saint-Domingue, quickly became one of the richest and most prosperous colonies in the world due to its production of sugar cane, coffee, cocoa and Indigo.
In 1791, a slaves rebellion led by Toussaint Louverture started. This eventually led to the independence of Haiti in 1804 and the eastern side of Hispaniola became known as Saint Domingue.
After the Haitian Revolution, many French settlers and slaveholders fled to the eastern part of the island, which was still under Spanish rule.
In order to maintain power in the colony and restore order, Spain granted more autonomy to the colony, which in some way Spain recognized French dominion over the island
In 1808, Napoleon Bonaparte invaded Spain and placed his brother Joseph on the throne. The Napoleonic Wars caused many problems for Spain and its European colonies. In an effort to keep the colony, Spain granted even more autonomy to Santo Domingo.
However, this was not enough to keep the colony and in 1821, Santo Domingo became one of many countries in Latin America to gain independence from Spain.
After years of struggle, Santo Domingo gained its own right from Spain and became the Dominican Republic in 1844 under Dominican patriot Juan Pablo Duarte, its founding father.
Major Cities
The Dominican Republic’s major cities are :
- Santo Domingo – The capital of the Dominican Republic and the largest city in the nation. It is also the oldest city in America, founded by Christopher Columbus in 1496.
- La Romana – A coastal city located in the southeast of the Dominican Republic. It is a popular tourist destination due to its beaches and resorts.
- Puerto Plata – A port city located on the north coast of the Dominican Republic. It is a popular tourist destination for its beaches, resorts and historic sites such as Fortaleza San Felipe de Puerto Plata, an old Spanish fort. The Dominican Republic provided religious freedom and even sheltered to Jews who escaped Nazi Germany and founded the city of Sosúa, in Puerto Plata.
- Santiago de los Caballeros – Along with Santo Domingo, these are the two major cities in the Dominican Republic, located in the center of the country. It is a major industrial center and the home of many universities and colleges.
- Punta Cana – A resort city located on the east coast of the Dominican Republic. It is a popular tourist destination for its beaches and resorts.
- Samaná – Located on the northeast coast of the Dominican Republic. Also known as the Samaná Peninsula, it is a popular tourist destination for its beaches, whale watching and hiking.
- San Francisco de Macorís – A city located in the northeast of the Dominican Republic. It is a major agricultural center, known for its production of coffee, cocoa and tobacco.
- Higuey – A city located in the northeast of the Dominican Republic. It is known for its many churches, including the Basilica of Our Lady of Higuey, the second largest church in the country.
- San Cristobal – The city located in the southwest of the Dominican Republic. San Cristobal is a major industrial center and the home of many universities and colleges.
- San Pedro de Macoris – A city located in the southeast of the Dominican Republic. San Pedro de Macoris is a major industrial center and the home of many universities and colleges.
- La Vega – A city located in the central part of the Dominican Republic. La Vega is known for its agriculture, particularly tobacco and coffee.
- Jarabacoa – A city located in the central part of the Dominican Republic. It is known for its agriculture, particularly coffee, and for its many rivers and waterfalls.
- Moca – A city located in the northwestern part of the Dominican Republic. It is an important agricultural center, known for its production of coffee, cocoa and tobacco.
- San Juan de la Maguana – A city located in the northwestern part of the Dominican Republic. It is an important agricultural center, known for its production of coffee, cocoa and tobacco.
- Cotuí – A city located in the northwestern part of the Dominican Republic. It is an important agricultural center, known for its production of coffee and cocoa.
- Bonao – A city located in the central part of the Dominican Republic. It is known for its agriculture, particularly coffee and tobacco.
- Salcedo – A city located in the northwestern part of the Dominican Republic. It is an important agricultural center, known for its production of coffee, cocoa and tobacco.
- Boca Chica – A town located in the southeast of the Dominican Republic. It is a popular tourist destination for its beaches, resorts and water sports.
- Río San Juan – A town located in the northeast of the Dominican Republic. It is a popular tourist destination for its beaches, fishing and boat tours.
- Monte Cristi – A town located in the northwest of the Dominican Republic. It is a popular tourist destination for its beaches, fishing and diving.
- Navarrete – A town located in the central part of the Dominican Republic. It is known for its agriculture, particularly coffee and tobacco.
- San José de Ocoa – A town located in the southwest of the Dominican Republic. It is known for its agriculture, particularly coffee and cocoa.
- Constanza – A town located in the central part of the Dominican Republic. It is known for its agriculture, particularly coffee and tobacco.
Geography
The Caribbean country consists of several mountain ranges, including the Cordillera Central, the Sierra de Neiba and the Cordillera Septentrional.
The largest rivers include the Yaque del Norte, the Nizao, the Soco the Bajabonico, and the Ozama river (rio Ozama). Out of those, the largest river is the Yaque del Norte. Dozens of smaller rivers and streams drain the country from the mountains to the sea.
The smaller rivers include the Jimenoa, the Yuna, the San Juan and the Sabaneta.
The highest point in the country is Pico Duarte, which is 3,098 meters (10,164 feet) above sea level. The capital city of Santo Domingo is located on the Caribbean coast.
The terrain of the Dominican Republic is incredibly diverse, with arid deserts, tropical rainforests, mangrove swamps and alpine ranges.
Beaches abound too, and most of the best luxury resorts are situated on the north and east coasts.
Depending on where you go, you’ll find colonial architecture, sugar plantations, quaint villages, mountain retreats and much more.
The Dominican Republic has natural hazards, which include periodic droughts. However there is also occasional flooding, due to the fact that the country lies in the middle of the hurricane belt and is subject to severe storms from June to October.
Mountain ranges
The country has several mountain ranges full of tropical rainforests, the most important of which are the Cordillera Central, the Sierra de Neiba and the Cordillera Septentrional.
The Cordillera Central is the largest and highest mountain range in the Dominican Republic. It extends for about 150 kilometers (93 miles) across the country, from the northwest to the southeast. The highest peak in the Cordillera Central is Pico Duarte, which is 3,098 meters (10,164 feet) above sea level.
The Sierra de Neiba is a mountain range located in the southwest of the Dominican Republic. It extends for about 100 kilometers (62 miles) from west to east. The highest peak in the Sierra de Neiba is Pico Yaque, which is 2,760 meters (9,055 feet) above sea level.
The Cordillera Septentrional is a mountain range located in the north of the Dominican Republic. It extends for about 80 kilometers (50 miles) from west to east. The highest peak in the Cordillera Septentrional is Pico Diego de Ocampo, which is 2,686 meters (8,820 feet) above sea level.
Lakes and Lagoons
The Dominican Republic has many lakes and lagoons, called lagunas in Spanish, among you can find:
- Lake Enriquillo – as the largest lake in the Dominican Republic, the Lago Enriquillo and the lowest point in the Caribbean.
- Laguna de Oviedo – The largest lagoon in DR, with a salt-water level three times higher than that of the sea, Laguna de Oviedo is a prime bird watching area. Around the lagoon’s thick mangrove swamps and 24 keys you’ll spot royal and blue herons, the great egret, roseate spoonbills, sandpipers, and flamingos.
- Laguna Dudú – It’s time to go Kayaking! Rent a kayak and explore the turquoise waters of Laguna Dudú. You can take it easy with your trusty sidekick or hit up one those ziplines that look like they’re set up by kids who couldn’t be more than 10 feet tall but are still super cool (and maybe even dangerous).
- Laguna Gri – Gri – If you’re a fan of birds, one of the best places to see them is at one of the DR’s major bird sanctuaries. Set along a peaceful lagoon, the sanctuary is full of different species of birds, including egrets and vultures. You can take a boat ride through the lagoon to get up close and personal with the birds, and at sunset, you’ll get to see them in their natural habitat as they fly and chirp above the mangroves. It’s an experience you won’t soon forget!
- Laguna de Rincón – It is the country’s largest freshwater lagoon, reaching 28 square kilometers (11 square miles). The lagoon is home to a variety of flora and wildlife, making it a protected scientific reserve. The lagoon is a popular spot for bird watching, as it is home to water turtles, iguanas, flamingos, pelicans, herons, and Florida ducks. Visitors to the lagoon can also enjoy swimming, fishing, and kayaking. Laguna Rincón is a beautiful place to relax and enjoy the natural beauty of the Dominican Republic.
Climate
The climate of the Dominican Republic is tropical, with an average yearly temperature of 26 degrees Celsius (79 degrees Fahrenheit).
As a tropical country, other places besides the beach are on the cold side of the spectrum. In Contanza, the average yearly temperature is 18 degrees Celsius (64 degrees Fahrenheit).
There are two seasons in the Dominican Republic: the rainy season and the dry season. The rainy season goes from May to November, and the dry season goes from December to April.
During the rainy season, it rains almost every week, usually in the afternoon or at night. The average rainfall is about 1000 mm (39 inches) per year.
During the dry season, there is very little rain. The average rainfall during this time is about 500 mm (20 inches) per year.
The Dominican Republic is located in the hurricane belt, so it is vulnerable to hurricanes from June to November.
Hurricanes that have hit the Dominican Republic include Hurricane Georges in 1998,
Dominican Economy
The country is second largest in terms of area in the Caribbean region after Cuba; besides, Dominican Republic has also second largest economy in the Caribbean and Central American region. By virtue of having year-round golf course and also having beautiful beaches and other tourists’ points, the Dominican Republic is the Caribbean’s largest tourist destination.
It exports sugar, coffee, cocoa, tobacco, light manufactures, and minerals. It also exports ferronickel, gold, and silver. The country imports petroleum products, foodstuffs, clothing, and other consumer goods.
Major industries of Dominican Republic include tourism, agriculture, mining, manufacturing of cigarettes and cigars; assembly of electrical components; sugar refining, steel fabrication; textile and apparel manufacturing, and tourism.
Agriculture
The Dominican Republic has a variety of agricultural products, including coffee, cocoa, tobacco, rice, beans, potatoes, corn, milk, eggs, beef, poultry, and fishing.
It exports coffee, cocoa, tobacco, sugar, rice, beans, eggs, dairy products, and beef. The country also exports citrus fruits, melons, bananas, and vegetables.
The Dominican Republic imports wheat, vegetable oils, soybeans, corn, animal feed, and petroleum products.
Currency
Be ready to use the Dominican peso in the Dominican Republic, the official currency. However, US dollars are also widely accepted in the national district, and especially in the tourist areas.
The exchange rate is approximately 1 US dollar to 55 Dominican pesos as of June 2022.
Refer to our currency converter on the link below and be ready to pay cash on restaurants and other places
Language
Spanish is the official language of the Dominican Republic, but English is also widely spoken, particularly in the tourist areas.
Some helpful Spanish phrases:
“Hola, ¿Cómo estás?” – “Hello, how are you?”
“¿Qué tal?” – “How are you?”
“Bien, gracias” – “Fine, thank you”
“De nada” – “You’re welcome “
“Por favor” – “Please”
“Gracias” – “Thank you”
“Disculpe” – “Excuse me”
Climate
The climate of the Dominican Republic is tropical, with average temperatures ranging from 18-26 degrees Celsius (64-79 Fahrenheit).
The rainy season is from May to November and the hurricane season is from June to November.
Natural Resources
The Dominican Republic has many natural resources, including:
- Fertile agricultural land – The Dominican Republic has some of the most fertile agricultural land in the world.
- Minerals – The Dominican Republic has deposits of gold, silver, copper, iron and manganese.
- Water – The Dominican Republic has many rivers and lakes,
What is the Dominican Republic known for?
The Dominican Republic is known for its beaches, resorts, and tourism. It is also known for its baseball players, including some of the most famous in Major League Baseball (MLB). Additionally, the Dominican Republic is known for its music, food, and culture.
What are some interesting facts about the Dominican Republic?
The Dominican Republic is home to over 10 million people.
After the Haitian Revolution in 1804, the western part of the island became the independent country of Haiti and the eastern part remained a Spanish colony until 1821.
In 1821, the Dominicans declared independence from Spain but were soon occupied by Haiti. In 1844, they regained their independence.
Between 1861 and 1865, they again became a colony of Spain. In 1865, they once more gained their independence and in 1869 changed their name to “Dominican Republic”.
Geography of Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic is located on the Caribbean island of Hispaniola, which it shares with Haiti. The country occupies an area
In 1844, the country’s name was changed to “Dominican Republic” to highlight its link to Catholicism.
Population of the Dominican Republic
The population of the Dominican Republic is estimated at 10,847,910 million people (2020), making it the second most populous country in the Caribbean after Cuba.
The capital city is Santo Domingo with a population of 3 million people.
The official language is Spanish but you will find that English is widely spoken as well.
Most of the population (80%) is of mixed race, 14% is black and 6% is white.
Religion in the Dominican Republic
The majority of the population in the Dominican Republic is Roman Catholic (78%), with Protestants accounting for 16% and other religions 6%.
Frequently asked questions about the Dominican Republic
Where exactly is the Dominican Republic located?
GPS Coordinates of the Dominican Republic With a latitude of 18.7357° N and a longitude of 70.1627° W, the Dominican Republic is located above the equator.
The GPS coordinates of the DR shows that the country is positioned in the northern and western hemispheres.
Is the Dominican Republic part of the USA?
No, the Dominican Republic is not part of the United States of America. It is an independent country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean Sea.
What kind of government does the Dominican Republic have?
The Dominican Republic is a democratic republic with a presidential system of government.
Where is the Dominican Republic in the Caribbean?
The Dominican Republic is a large country located in the north-central Caribbean; occupying the eastern two-thirds of the Island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago. It is positioned in the Northern and Western hemispheres of the Earth.
Where is the Dominican Republic next to?
The Dominican Republic is bordered by Haiti to the west, the Atlantic Ocean to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the south, and the Mona Passage (Canal de la Mona), which separates the nation to Puerto Rico to the east.
Together with Haiti, it forms the island of Hispaniola.
What type of government the Dominican Republic has?
The government type of the Dominican Republic is a representative democracy or democratic republic under which there are three branches of power: executive, legislative, and judicial. Furthermore, the country is second largest in terms of area in the Caribbean region after Cuba; besides, Dominican Republic has also second largest economy in the Caribbean and Central American region after Mexico.
The Dominicans have two legislative houses: Senate, with 32 representatives and the Chamber of Deputies with 190.
Where is Dominican Republic in the World?
The Dominican Republic is a country located in the Caribbean Region of the world. As part of the Greater Antilles Archipelago, the Dominican Republic is the second largest country in the Caribbean,
Related – What time is it in the Dominican Republic?
Now that we have answered your question “Where is the Dominican Republic located?” it’s time to start planning and packing your bags to get ready for an amazing trip!
Whether you’re looking for a romantic getaway, a family vacation, business, medical tourism, or just some fun in the sun, the Dominican Republic is the perfect place for you.
Click the country name on the search bar to find more information about it.
Also, subscribe to our YouTube channel at Dominican Travel Pro!
Stay Pro.